
Now, the structure on the right is the cyclic form of D-Glucose which, as a six-membered ring adopts a chair conformation. Interestingly, this new asymmetric center is formed in both configurations:Ĭarbon 1 is the new stereogenic center shown with a wiggly line which means the formation of both configurations. For example, the linear D-Glucose converts into a pyranose ring through the attack of C5-OH group on the carbonyl forming a new asymmetric center. They are formed through an intramolecular hemiacetal formation.

These rings are classified as a furanose and a pyranose ring respectively which is a general nomenclature for oxygen-containing 5– 6-membered rings. On the other hand, D -glucose and D-galactose are epimeric at carbon-4 since that is the only stereogenic center with an opposite configuration:Ĭarbohydrates exist also in a cyclic form and this is especially favored when 5- 6-membered rings can be formed. So, D-Glucose and D-mannose are epimers and to specify, we can say that they are epimeric at carbon-2. Of course, there should be more than one chiral center, otherwise, the change of one would indicate a pair of enantiomers. Now, diastereomers that differ in the configuration of only one chiral center are called epimers. For example, while the D and L-Glucoses are enantiomers, D-Glucose and D-mannose are diastereomers since the configuration of only one stereogenic center (C2) is changed: As a reminder, all the stereogenic centers are inverted when comparing D and L isomers since they are enantiomers and any other pair of stereoisomers represents diastereomers. ↑ Solano Community College (2007) Drawing Haworth Projections.In the previous post, we listed most of the naturally occurring D aldoses and ketoses together with their enantiomeric L isomers.↑ Russel KC (1999) Haworth Projections.

ANOMERIC CARBON IN STRAIGHT CHAIN PROFESSIONAL
↑ Professional Education,Testing and Certification Organization International (2012) Organic Chemistry 16.4 Cyclic Structures of Monosaccharides.↑ Cornell College (2012) Reactions of monosaccharides.(2012) Biochemistry, 7th Edition, New York: Kate Ahr Parker. Ī Condensation reaction catalyses the formation of disaccharides between 2 monosaccharides with the elimination of a water molecule.ĭetermining which anomer is alpha and which is beta is easy when looking at the Haworth projection alpha anomers have different stereochemistry at carbon 1 and carbon 5, whereas beta anomers have the same stereochemistry at carbon 1 and 5. Under a dynamic equilibrium, 6-carbon pyranose rings are usually formed as compared to 5-carbon furanose rings. Anomers in the form of Fischer projection (open-chain sugar) makes up less than 1% of the total solution. The percentages of each type of anomers present are as follow: 25% are alpha anomers and 75% are beta anomers. The reaction is said to be at a dynamic equilibrium, where the rate of forward reaction is equal to the rate of backward reaction. In addition, these straight chain sugars are converted back into its ring structure. Through contact with water, the sugar monomers appear to be opening up their ring structure to form straight chain sugars. In the process of mutarotation, a solution of both anomers are heated at a high temperature, giving rise to individual monomers. Īlpha and beta anomers are formed from an open-chain sugar by mutarotation.
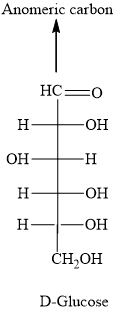
It is possible to distinguish the two by the directions that the molecule rotates under plane-polarise light. A beta-glucose has its -OH parallel to the ring. An alpha-glucose has its -OH perpendicular to the ring. Thus, the carbon is called an anomeric carbon. They are identified by the direction that the -OH group is pointing to on the first carbon (C1) on the cyclic sugar. There are 2 forms of anomers, namely alpha and beta. As the name suggests, they are isomers of each other.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
